






Cable Glands and Terminal Lugs: Essential Components for Electrical Connectivity
Introduction
Polycab is dedicated to make life better with an extensive range of electrical wire and cables that are manufactured in plants using latest technology (electron beam/buss co-kneaders) with world-class materials under strict quality assurance procedures with total traceability of in-house or approved supplier materials and throughout production processes. The Polycab R & D center is the backbone for compound and metals innovative developments to provide optimum power, weight savings coupled with superior fire performance that assures compliance with all local and international standards validated by comprehensive testing at polycab internal NABL accredited lab and external third-party labs.

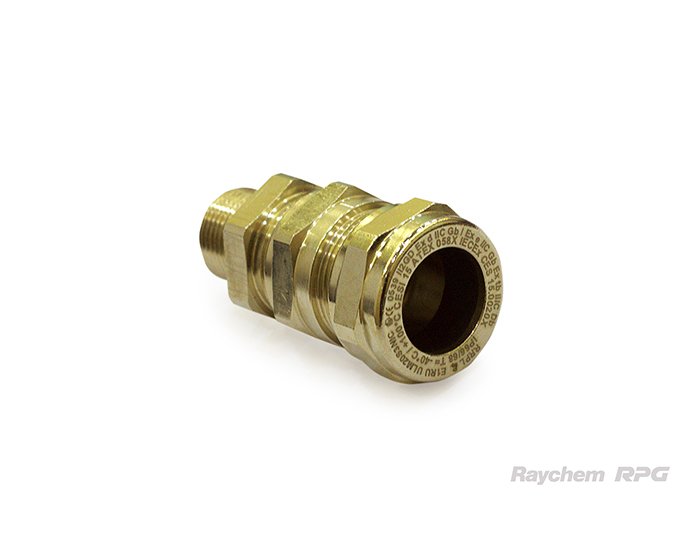
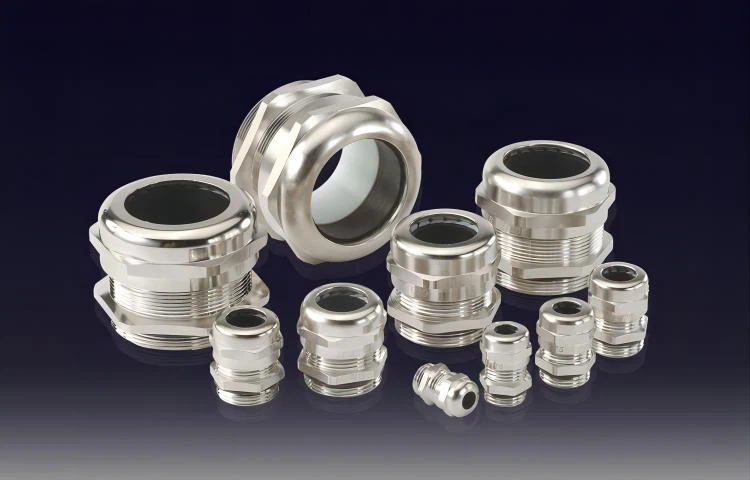
Cable Glands
Functions and Importance
Cable glands, also known as cable connectors or cable fittings, serve several essential functions:
- Sealing and Protection: Cable glands provide a secure seal around the cable entry point, preventing the ingress of dust, dirt, moisture, and other contaminants. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the electrical connection, especially in harsh environments.
- Strain Relief: They offer strain relief by clamping onto the cable, which prevents excessive pulling or twisting that could damage the cable or disconnect it from the terminal.
- Grounding and Bonding: In certain applications, cable glands provide a means for grounding and bonding the cable, ensuring electrical safety and compliance with regulatory standards.
Types of Cable Glands
Cable glands come in various types, each suited for different applications and environments
- Material-Based Classification:
- Metallic Cable Glands: Made from brass, stainless steel, or aluminum, these glands offer robust protection and are ideal for industrial and outdoor applications where durability is a concern.
- Non-Metallic Cable Glands: Typically made from plastic or nylon, these glands are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and suitable for less demanding environments.
- Application-Based Classification:
- Explosion-Proof Cable Glands: Designed for hazardous environments where there is a risk of explosion, these glands are used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and mining.
- EMC Cable Glands: These provide electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) protection, minimizing electromagnetic interference (EMI) in sensitive electronic installations.
- Entry System-Based Classification:
- Single-Entry Cable Glands: Designed for single cable entry, these are the most common type used in various applications.
- Multi-Entry Cable Glands: Allowing multiple cables to pass through a single gland, these are used in situations where space is limited, and multiple connections are needed.
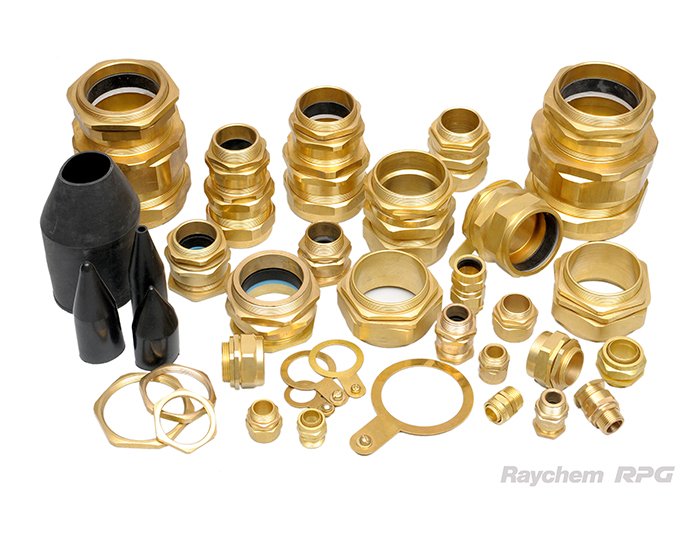



Category A
Euro Series Cable Glands
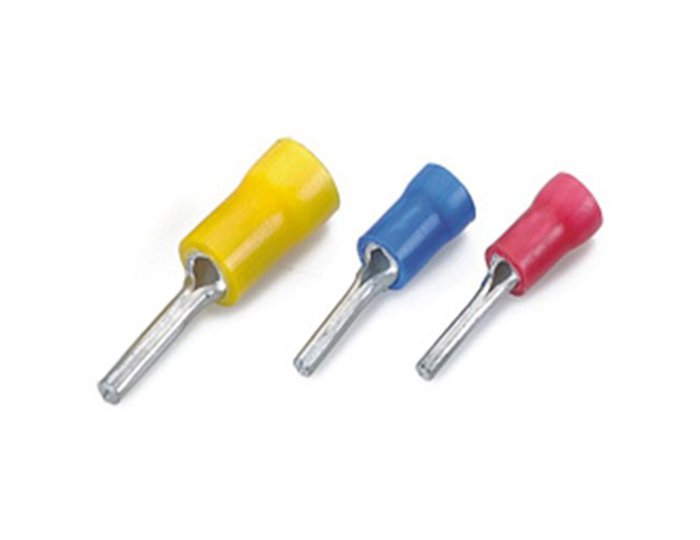
RLPI - Insulated Pin Type Terminals
Applications
Cable glands are used in numerous industries and applications, including:
- Industrial Machinery: Ensuring secure and reliable connections in heavy machinery.
- Automotive: Protecting wiring harnesses and electrical connections in vehicles.
- Telecommunications: Safeguarding cables in communication networks.
- Renewable Energy: Providing durable connections in solar and wind power installations.

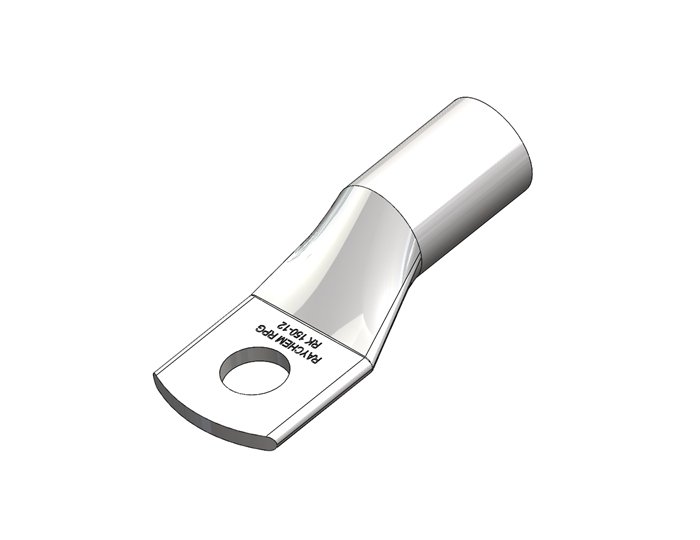
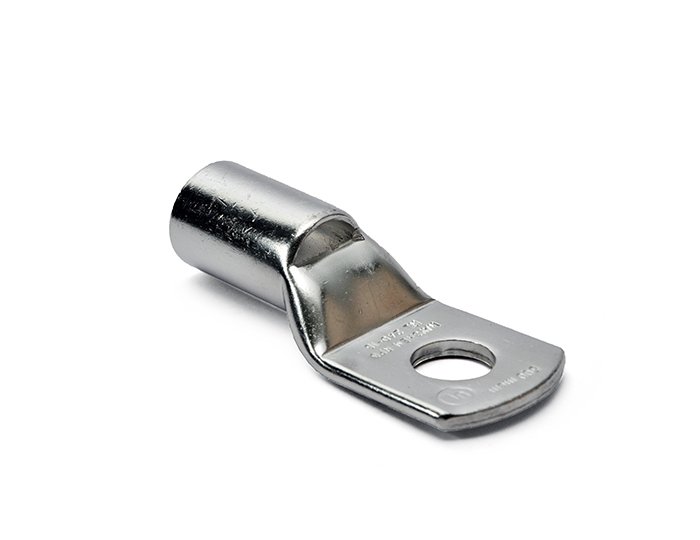
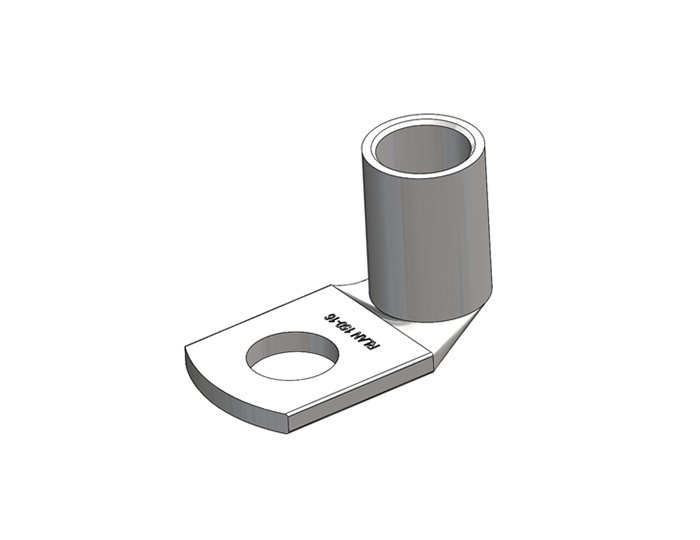
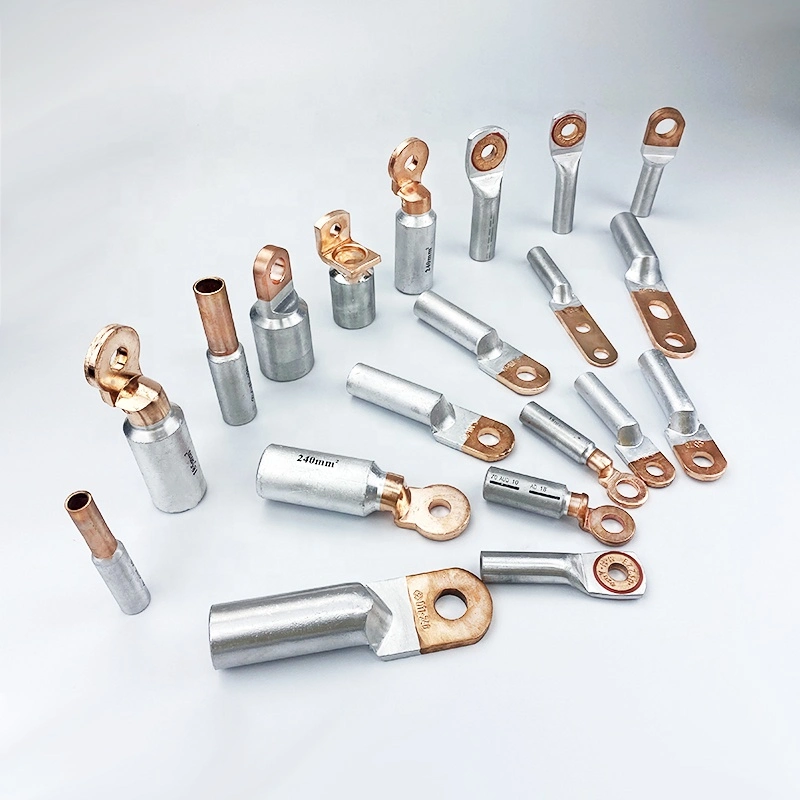
Terminal Lugs
Functions and Importance
Terminal lugs, also known as cable lugs or electrical lugs, are connectors used to securely attach cables to electrical devices, equipment, or other cables. Their primary functions include:
- Secure Connection: Terminal lugs ensure a stable and reliable connection, which is essential for maintaining electrical continuity and preventing disconnections.
- Ease of Installation: They simplify the process of connecting and disconnecting cables, making maintenance and repairs more manageable.
- Current Carrying Capacity: Terminal lugs are designed to handle specific current ratings, ensuring that electrical connections can safely carry the required load without overheating.

Types of Terminal Lugs
Terminal lugs are categorized based on various factors, including their design, material, and method of attachment:
- Material-Based Classification:
- Copper Lugs: Highly conductive and commonly used in most electrical applications.
- Aluminum Lugs: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, suitable for specific applications where weight is a concern.
- Design-Based Classification:
- Ring Type Lugs: Feature a ring-shaped terminal end that can be securely bolted to a terminal block or stud.
- Fork Type Lugs: Have a fork-shaped end that allows for easy attachment and removal without completely removing the bolt.
- Pin Type Lugs: Designed with a pin-shaped terminal that fits into terminal blocks or other connectors.
- Attachment Method-Based Classification:
- Crimping Lugs: Attached to the cable using a crimping tool, providing a secure and permanent connection.
- Soldering Lugs: Attached by soldering, offering a reliable and conductive connection.
- Mechanical Lugs: Use screws or bolts for attachment, allowing for easy installation and removal.
Applications
Terminal lugs are widely used across various sectors:
- Power Distribution: Connecting cables in electrical panels, switchgear, and transformers.
- Telecommunications: Ensuring secure connections in communication networks.
- Automotive: Connecting battery cables and other electrical components in vehicles.
- Industrial Equipment: Providing reliable connections in machinery and equipment.

Conclusion
Cable glands and terminal lugs are fundamental components in the realm of electrical installations. Their roles in providing secure connections, protection, and strain relief cannot be overstated. By understanding the different types and applications of these components, professionals in the electrical industry can make informed decisions to ensure the safety, reliability, and efficiency of their electrical systems. Whether in industrial settings, automotive applications, or telecommunications, the proper selection and use of cable glands and terminal lugs are crucial for achieving optimal performance and longevity of electrical installations.
